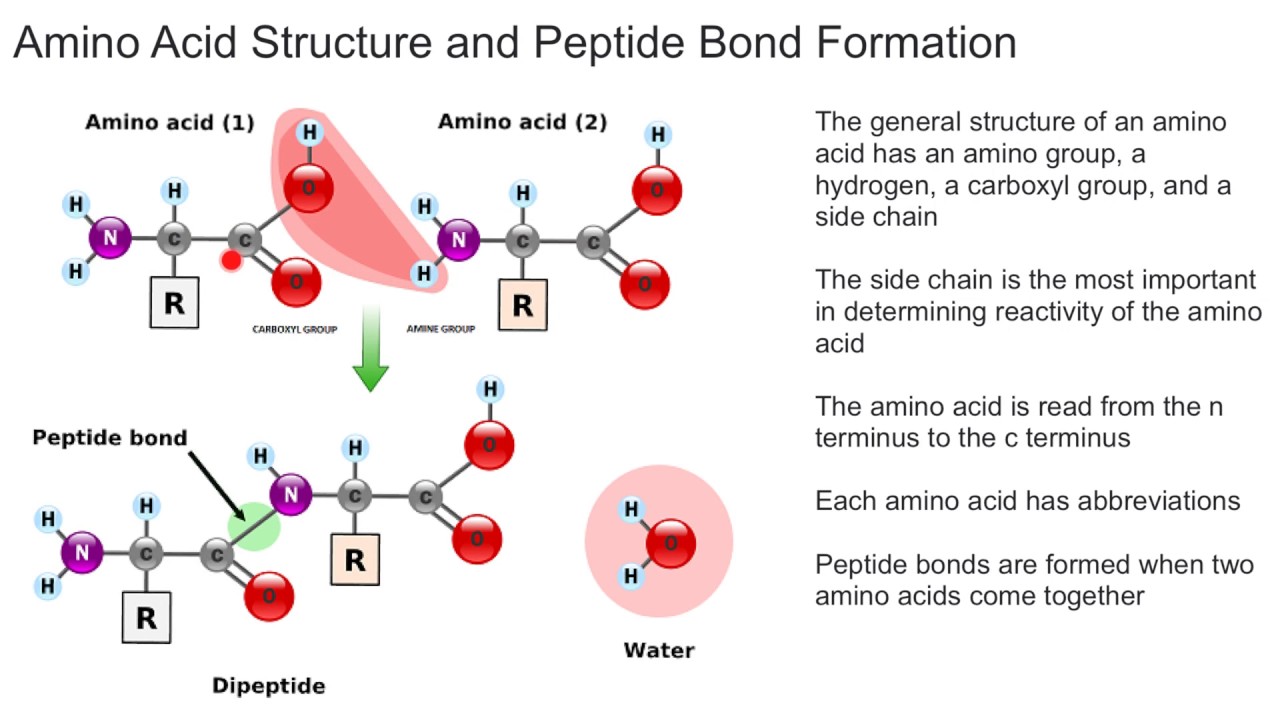
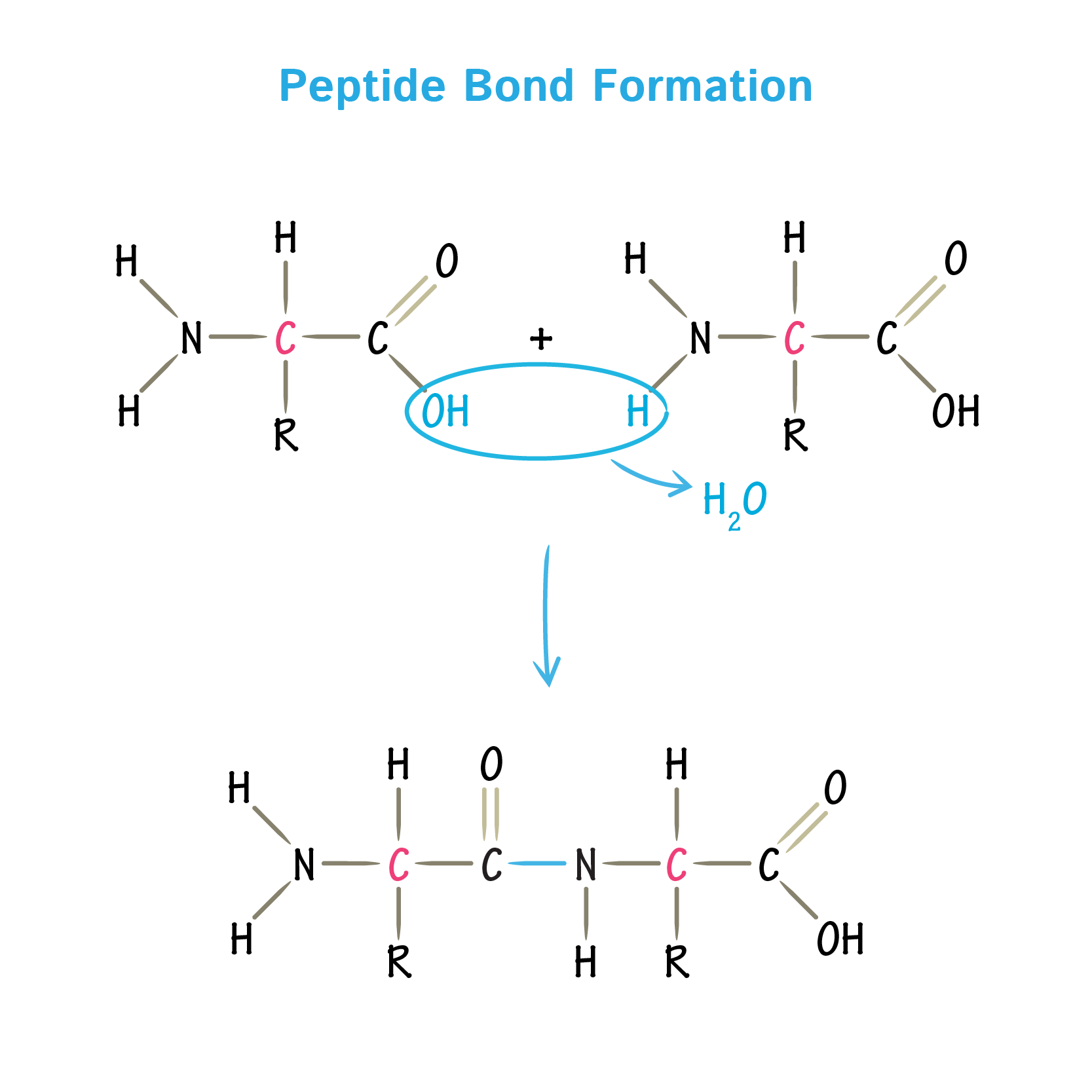
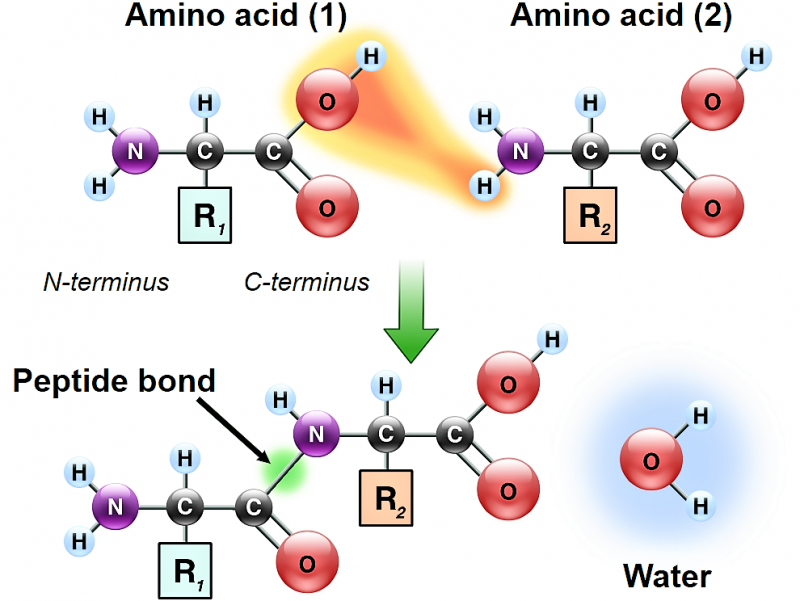
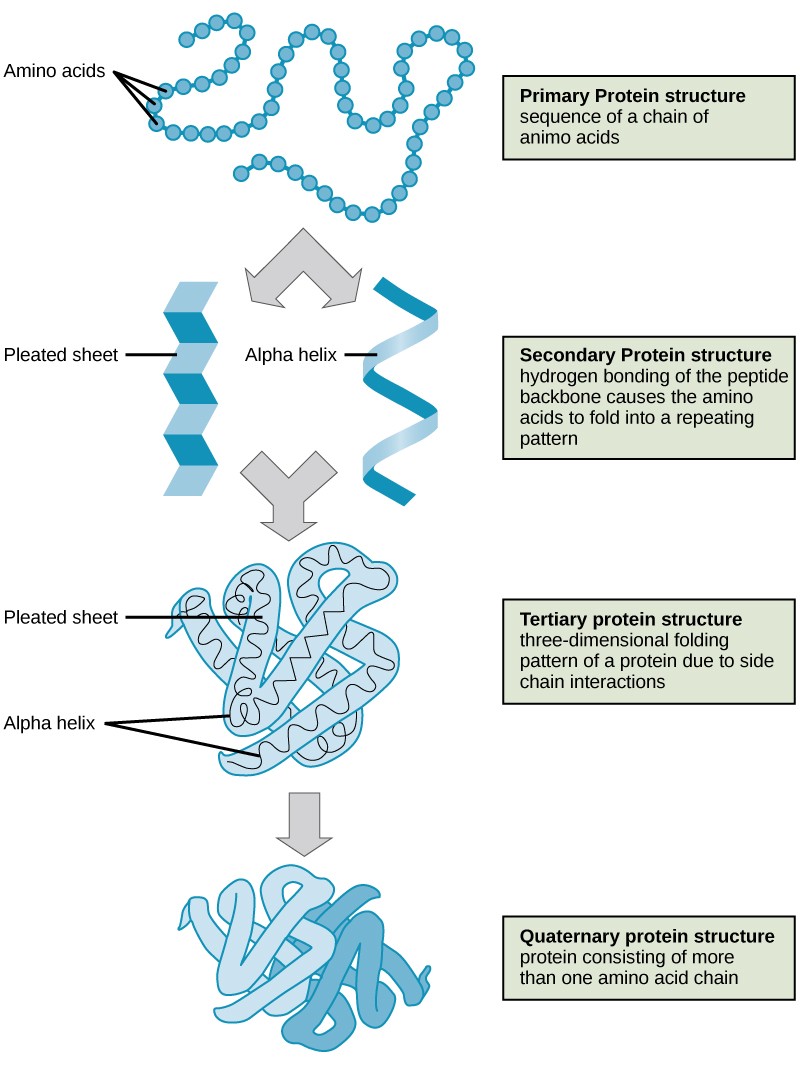
Amino Acids Bond Together To Form
Amino Acids Bond Together To Form - They play an extensive role in gene expression process, which includes an adjustment of protein functions that facilitate messenger rna (mrna) translation (scot et al., 2006). Web the essential amino acids are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Web two amino acids, serine and threonine, contain aliphatic hydroxyl groups (that is, an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, represented as ―oh). The amino acids of a polypeptide are attached to their neighbors by covalent bonds known as a peptide bonds. Web but how are amino acids actually linked together in chains? After they are incorporated into a peptide, the individual amino acids are referred to as amino acid residues. The r group varies among amino acids and determines the differences between these protein monomers. Web when two amino acids form a dipeptide through a peptide bond, [1] it is a type of condensation reaction. The r groups of the amino acids stick outward from the α helix, where they are free to interact 3 ^3 3 cubed. Web amino acids joined by a series of peptide bonds are said to constitute a peptide.
The amino acid sequence of a protein is determined by the information found in the cellular genetic code. Small polymers of amino acids (fewer than 50) are called oligopeptides, while larger ones (more than 50) are referred to as polypeptides. The r group varies among amino acids and determines the differences between these protein monomers. They play an extensive role in gene expression process, which includes an adjustment of protein functions that facilitate messenger rna (mrna) translation (scot et al., 2006). The r groups of the amino acids stick outward from the α helix, where they are free to interact 3 ^3 3 cubed. Conditional amino acids include arginine, cysteine, glutamine, glycine, proline, and tyrosine. Additional amino acids are added in the same way, by formation of peptide bonds between the free carboxyl on the end of the growing chain and the amino group of the. Web the essential amino acids are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. The amino acids of a polypeptide are attached to their neighbors by covalent bonds known as a peptide bonds. Web all amino acids have the alpha carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, and amino group.
The r group varies among amino acids and determines the differences between these protein monomers. The nonessential amino acids are alanine, asparagine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and serine. Web this pattern of bonding pulls the polypeptide chain into a helical structure that resembles a curled ribbon, with each turn of the helix containing 3.6 amino acids. Web two amino acids, serine and threonine, contain aliphatic hydroxyl groups (that is, an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, represented as ―oh). The r groups of the amino acids stick outward from the α helix, where they are free to interact 3 ^3 3 cubed. Additional amino acids are added in the same way, by formation of peptide bonds between the free carboxyl on the end of the growing chain and the amino group of the. The amino acids of a polypeptide are attached to their neighbors by covalent bonds known as a peptide bonds. Web amino acids joined by a series of peptide bonds are said to constitute a peptide. Each bond forms in a dehydration synthesis (condensation) reaction. The amino acid sequence of a protein is determined by the information found in the cellular genetic code.
Peptide Bond Definition, Formation, Structure, Examples
The r groups of the amino acids stick outward from the α helix, where they are free to interact 3 ^3 3 cubed. Web when two amino acids form a dipeptide through a peptide bond, [1] it is a type of condensation reaction. The nonessential amino acids are alanine, asparagine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and serine. Each bond forms in.
Proteins are chains of amino acids. A) Structure of a typical amino
Web two amino acids, serine and threonine, contain aliphatic hydroxyl groups (that is, an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, represented as ―oh). Small polymers of amino acids (fewer than 50) are called oligopeptides, while larger ones (more than 50) are referred to as polypeptides. The r groups of the amino acids stick outward from the α helix, where.
The amino acids bond together to form which type of complex molecule? 1
Additional amino acids are added in the same way, by formation of peptide bonds between the free carboxyl on the end of the growing chain and the amino group of the. Web but how are amino acids actually linked together in chains? Web this pattern of bonding pulls the polypeptide chain into a helical structure that resembles a curled ribbon,.
Proteins — Overview & Importance in Biology Expii
The r group varies among amino acids and determines the differences between these protein monomers. Web all amino acids have the alpha carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, and amino group. Web the essential amino acids are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. After they are incorporated into a peptide, the individual amino acids.
Amino Acid Structure and Peptide Bond Formation YouTube
Web amino acids are a crucial, yet basic unit of protein, and they contain an amino group and a carboxylic group. Web amino acids are linked to each other by peptide bonds, in which the carboxyl group of one amino acid is joined to the amino group of the next, with the loss of a molecule of water. After they.
Two amino acids are joined together by
Web when two amino acids form a dipeptide through a peptide bond, [1] it is a type of condensation reaction. Additional amino acids are added in the same way, by formation of peptide bonds between the free carboxyl on the end of the growing chain and the amino group of the. Web this pattern of bonding pulls the polypeptide chain.
Amino acids physical, chemical properties and peptide bond
The amino acids of a polypeptide are attached to their neighbors by covalent bonds known as a peptide bonds. Each bond forms in a dehydration synthesis (condensation) reaction. Web all amino acids have the alpha carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, and amino group. Tyrosine possesses a hydroxyl group in the aromatic ring, making it a phenol derivative..
Enlace peptídico Qué es, características, cómo se forma, ejemplos
Conditional amino acids include arginine, cysteine, glutamine, glycine, proline, and tyrosine. The amino acids of a polypeptide are attached to their neighbors by covalent bonds known as a peptide bonds. Web this pattern of bonding pulls the polypeptide chain into a helical structure that resembles a curled ribbon, with each turn of the helix containing 3.6 amino acids. Web two.
Amino Acids Definition, Properties, Common Amino Acids Embibe
Web amino acids joined by a series of peptide bonds are said to constitute a peptide. Web two amino acids, serine and threonine, contain aliphatic hydroxyl groups (that is, an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, represented as ―oh). After they are incorporated into a peptide, the individual amino acids are referred to as amino acid residues. The r.
Chapter 3. Amino Acids & Proteins Introduction to Molecular and Cell
Each bond forms in a dehydration synthesis (condensation) reaction. After they are incorporated into a peptide, the individual amino acids are referred to as amino acid residues. They play an extensive role in gene expression process, which includes an adjustment of protein functions that facilitate messenger rna (mrna) translation (scot et al., 2006). Tyrosine possesses a hydroxyl group in the.
Web When Two Amino Acids Form A Dipeptide Through A Peptide Bond, [1] It Is A Type Of Condensation Reaction.
Web amino acids are linked to each other by peptide bonds, in which the carboxyl group of one amino acid is joined to the amino group of the next, with the loss of a molecule of water. The r groups of the amino acids stick outward from the α helix, where they are free to interact 3 ^3 3 cubed. Each bond forms in a dehydration synthesis (condensation) reaction. Web all amino acids have the alpha carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, and amino group.
The R Group Varies Among Amino Acids And Determines The Differences Between These Protein Monomers.
Web amino acids joined by a series of peptide bonds are said to constitute a peptide. The nonessential amino acids are alanine, asparagine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and serine. Web the essential amino acids are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Web but how are amino acids actually linked together in chains?
Conditional Amino Acids Include Arginine, Cysteine, Glutamine, Glycine, Proline, And Tyrosine.
Tyrosine possesses a hydroxyl group in the aromatic ring, making it a phenol derivative. Web amino acids are a crucial, yet basic unit of protein, and they contain an amino group and a carboxylic group. The amino acid sequence of a protein is determined by the information found in the cellular genetic code. After they are incorporated into a peptide, the individual amino acids are referred to as amino acid residues.
The Amino Acids Of A Polypeptide Are Attached To Their Neighbors By Covalent Bonds Known As A Peptide Bonds.
Web two amino acids, serine and threonine, contain aliphatic hydroxyl groups (that is, an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, represented as ―oh). They play an extensive role in gene expression process, which includes an adjustment of protein functions that facilitate messenger rna (mrna) translation (scot et al., 2006). Additional amino acids are added in the same way, by formation of peptide bonds between the free carboxyl on the end of the growing chain and the amino group of the. Web this pattern of bonding pulls the polypeptide chain into a helical structure that resembles a curled ribbon, with each turn of the helix containing 3.6 amino acids.