Beta Sheet Hydrogen Bonds
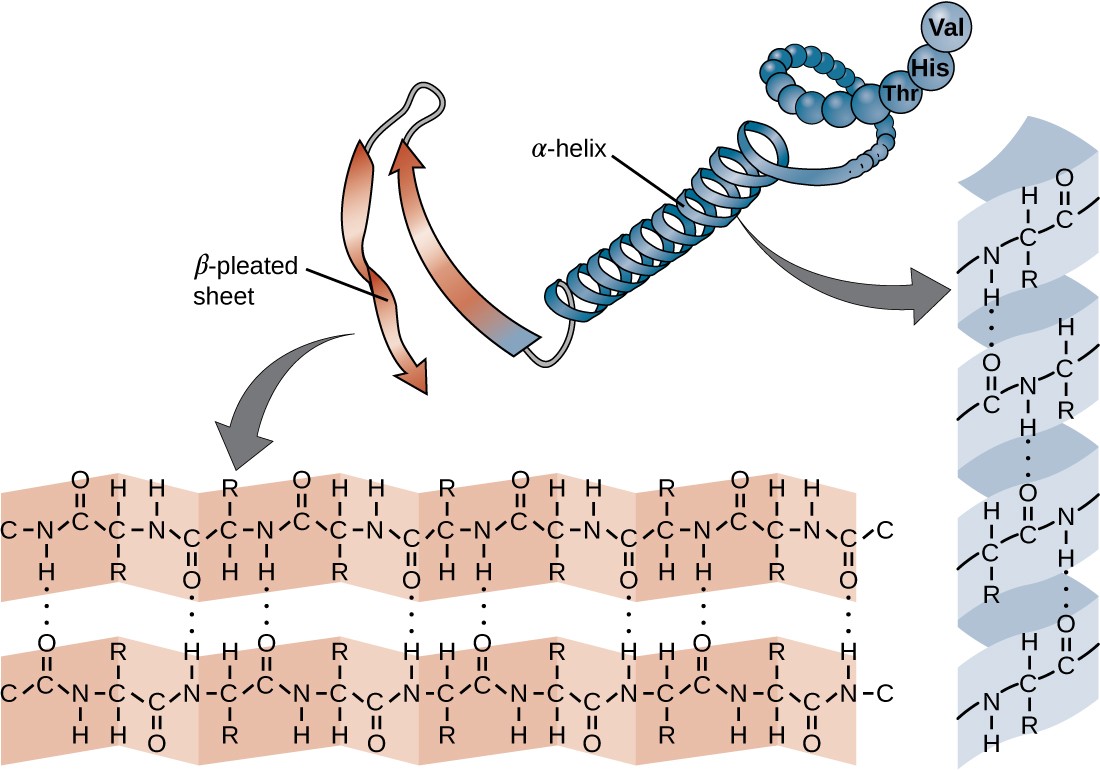
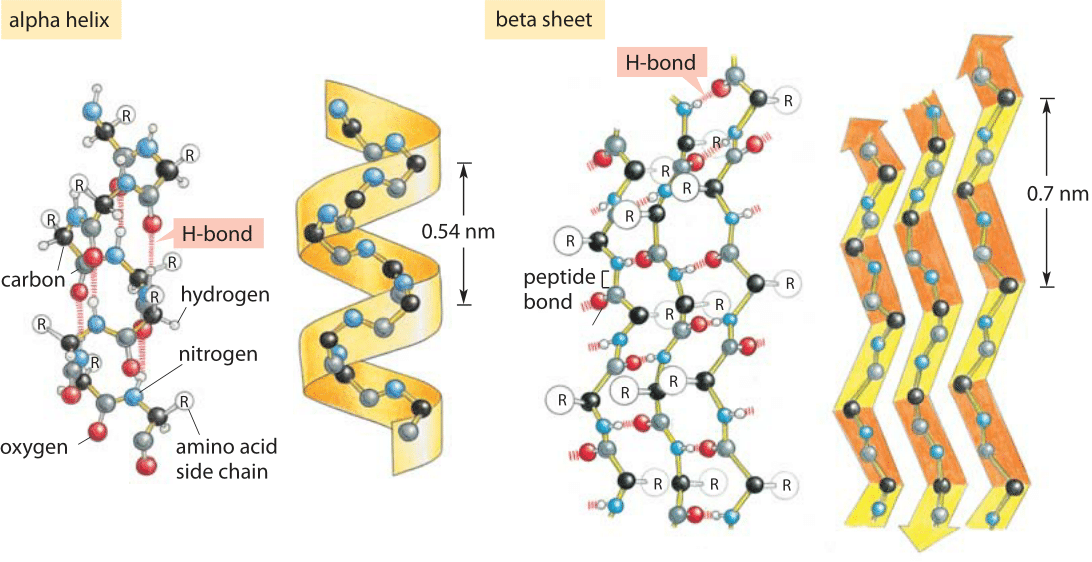
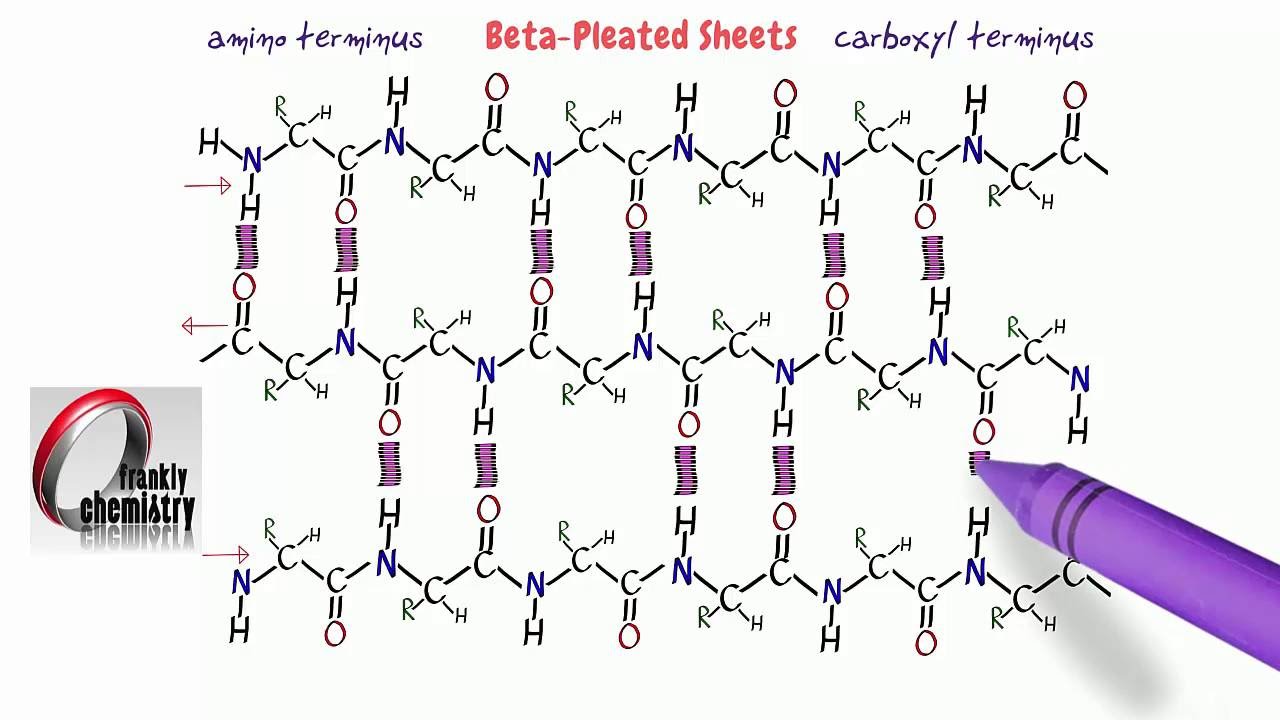
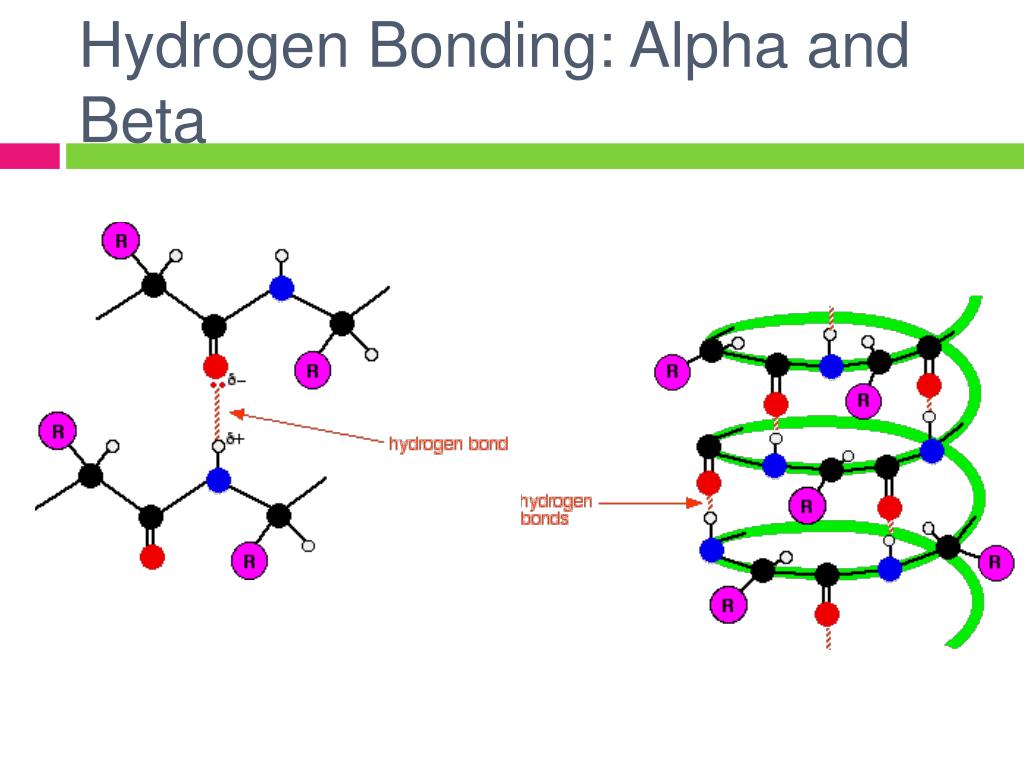
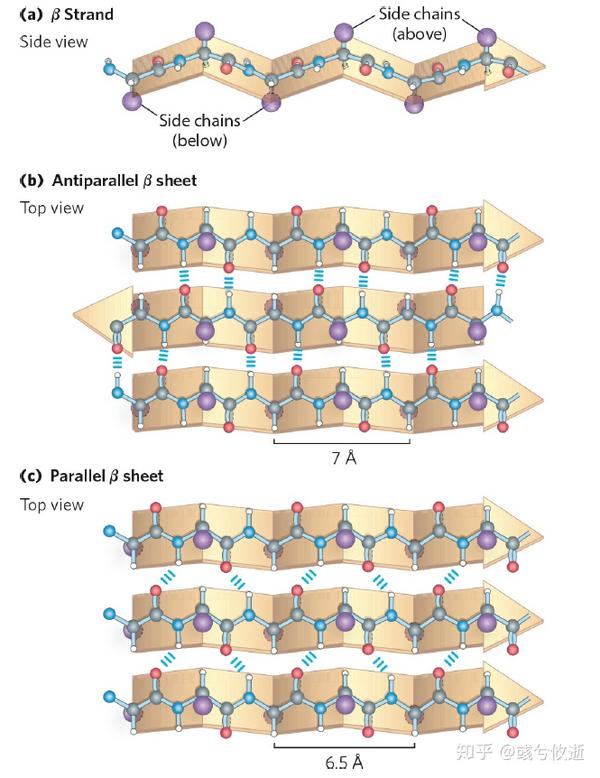
Beta Sheet Hydrogen Bonds - A helix with 2 residues/turn. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The figure to the left shows a. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. The hydrogen bonds are equally distanced. As a result they have to be separated by long sequence stretches. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. Web beta sheets ß sheets the other type of secondary structure pauling and corey discovered is the ß sheet.
The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. The hydrogen bonds are equally distanced. A helix with 2 residues/turn. The figure to the left shows a. Web beta sheets ß sheets the other type of secondary structure pauling and corey discovered is the ß sheet. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. As a result they have to be separated by long sequence stretches.
Web beta sheets ß sheets the other type of secondary structure pauling and corey discovered is the ß sheet. The hydrogen bonds are equally distanced. As a result they have to be separated by long sequence stretches. A helix with 2 residues/turn. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. The figure to the left shows a.
[Solved] How many hydrogen bonds involving the backbone CO and NH can
A helix with 2 residues/turn. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. The figure to the left shows a. The hydrogen bonds are equally distanced. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g.
7.4 Proteins Microbiology 201
The figure to the left shows a. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. A helix with 2 residues/turn.
PPT SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY Amino Acids and Proteins PowerPoint
A helix with 2 residues/turn. The figure to the left shows a. As a result they have to be separated by long sequence stretches. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. Web beta sheets ß sheets the other type of secondary structure pauling and corey discovered is the ß.
Hydrogen Bond Analysis Tutorial BioChemCoRe 2018
This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The hydrogen bonds are equally distanced. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. A helix with 2 residues/turn. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha.
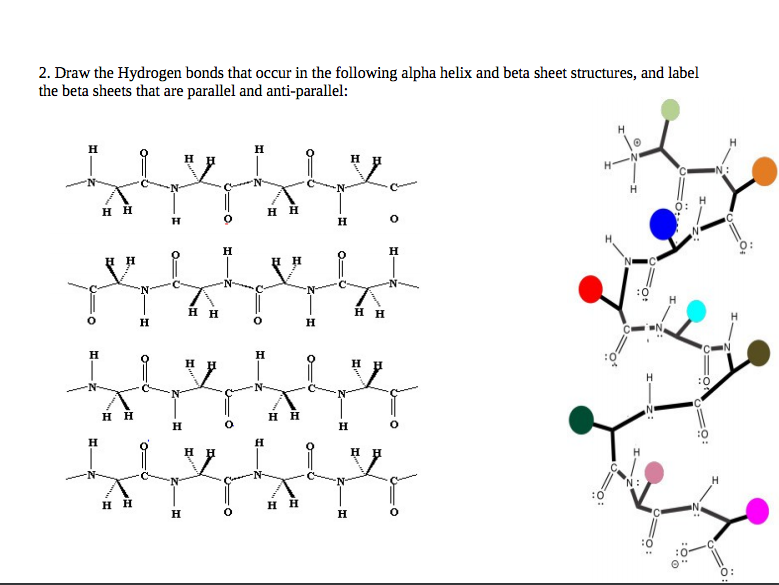
Solved 2. Draw the Hydrogen bonds that occur in the
A helix with 2 residues/turn. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. As a result they have to be separated by long sequence stretches.
Amino Acids 8. The betapleated sheets secondary structure of Proteins
As a result they have to be separated by long sequence stretches. Web beta sheets ß sheets the other type of secondary structure pauling and corey discovered is the ß sheet. The hydrogen bonds are equally distanced. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. The figure to the left.
PPT Proteins PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1460585
The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. A helix with 2 residues/turn. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The hydrogen bonds are equally distanced. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within.
20.15 Secondary Protein Structure Chemistry LibreTexts
The figure to the left shows a. A helix with 2 residues/turn. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. The hydrogen bonds are equally distanced. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha.
4.2 Protein Secondary Structure 知乎
The hydrogen bonds are equally distanced. The figure to the left shows a. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. A helix with 2 residues/turn.
Alpha Helix and Beta Sheet
A helix with 2 residues/turn. Web beta sheets ß sheets the other type of secondary structure pauling and corey discovered is the ß sheet. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen.
The Figure To The Left Shows A.
A helix with 2 residues/turn. Unlike the α helix, the ß sheet is formed by hydrogen bonds between protein strands, rather than within. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. The hydrogen bonds are equally distanced.
This Structure Occurs When Two (Or More, E.g.
As a result they have to be separated by long sequence stretches. Web beta sheets ß sheets the other type of secondary structure pauling and corey discovered is the ß sheet.
![[Solved] How many hydrogen bonds involving the backbone CO and NH can](https://cdn.testbook.com/images/production/quesImages/qImage646f23abed4806260c7a04d2.png)