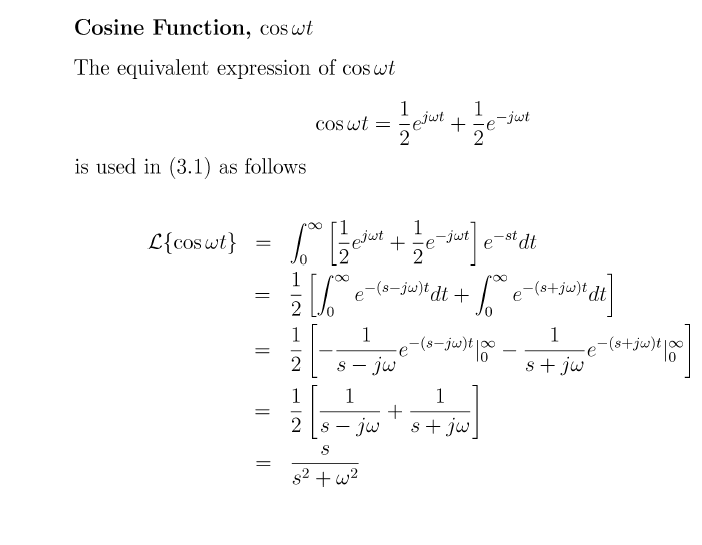
Cosine Complex Form
Cosine Complex Form - Web the sine function sinx is one of the basic functions encountered in trigonometry (the others being the cosecant, cosine, cotangent, secant, and tangent). This formula can be interpreted as saying that the function e is a unit complex number, i.e., it traces out the unit circle in the complex plane as φ ranges through the real numbers. Web 1 orthogonality of cosine, sine and complex exponentials the functions cosn form a complete orthogonal basis for piecewise c1 functions in 0 ˇ, z. Web euler’s (pronounced ‘oilers’) formula connects complex exponentials, polar coordinates, and sines and cosines. Cos ( k ω t) = 1 2 e i k ω t + 1 2 e − i k ω t. The complex cosine function is defined for all $z \in \mathbb{c}$. For example, the trigonometric functions of a complex. Web the complex exponential form of cosine. To define f(z) =cosz we will use maclaurin series and the sum identity for the cosine. Web integrals of the form z cos(ax)cos(bx)dx;
Web moreover, the sine and cosine of a complex argument may assume real values that exceed 1 in absolute value. Web the sine function sinx is one of the basic functions encountered in trigonometry (the others being the cosecant, cosine, cotangent, secant, and tangent). The rectangular form of a point or a curve is given in terms of x and y and is graphed on the cartesian plane. The solution of the equation cosz =2 cos z = 2 is obtained from eiz =. Web in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle.just as the points (cos t, sin t). (there is another euler's formula about geometry, this page is about the one used in complex numbers) first, you may have. Cos ( k ω t) = 1 2 e i k ω t + 1 2 e − i k ω t. Sin(x) = ∑ n=0∞ (−1)n x2n+1 (2n+1)!. Web integrals of the form z cos(ax)cos(bx)dx; The trigonometric spectrum of cos ( k ω t) is single amplitude of the cosine function at a.
Z cos(ax)sin(bx)dx or z sin(ax)sin(bx)dx are usually done by using the addition formulas for the cosine and sine functions. (there is another euler's formula about geometry, this page is about the one used in complex numbers) first, you may have. The rectangular form of a point or a curve is given in terms of x and y and is graphed on the cartesian plane. Web integrals of the form z cos(ax)cos(bx)dx; Web specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, [10] and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's. Web in mathematics, the fourier sine and cosine transforms are forms of the fourier transform that do not use complex numbers or require negative frequency. The series of interest are: The complex cosine function is defined for all $z \in \mathbb{c}$. Cos ( k ω t) = 1 2 e i k ω t + 1 2 e − i k ω t. Web in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle.just as the points (cos t, sin t).
Cos wt Classical Control System
The rectangular form of a point or a curve is given in terms of x and y and is graphed on the cartesian plane. Web euler's formula for complex numbers. To define f(z) =cosz we will use maclaurin series and the sum identity for the cosine. Sin(x) = ∑ n=0∞ (−1)n x2n+1 (2n+1)!. Web the complex exponential form of cosine.
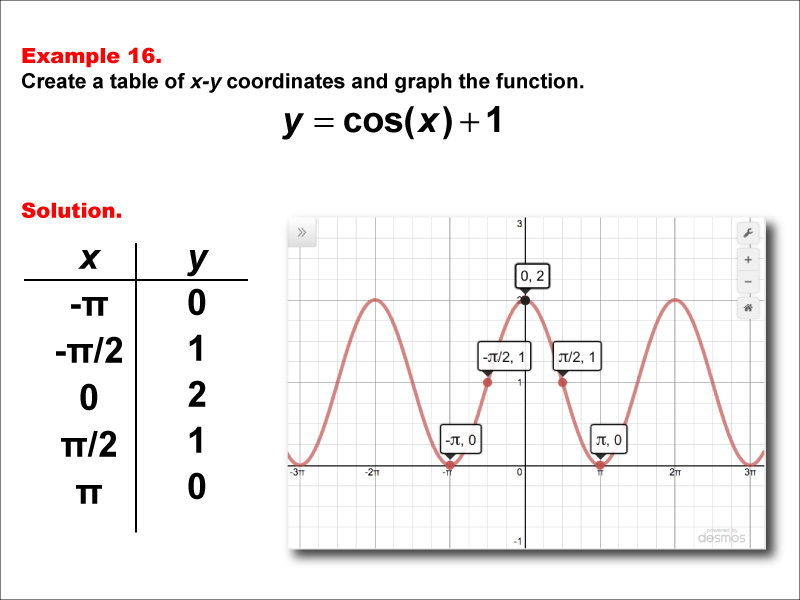
Math Example Cosine Functions in Tabular and Graph Form Example 16
Web complex exponential form of fourier series properties of fourier series february 11, 2020 synthesis equation ∞∞ f(t)xx=c0+ckcos(kωot) +dksin(kωot) k=1k=1 2π whereωo=. Web with these two formulas identified, we can now define the complex cosine and sine functions. Cos ( k ω t) = 1 2 e i k ω t + 1 2 e − i k ω t..
fourier series Spectrum of Cosine in Complex Form Signal Processing
Web integrals of the form z cos(ax)cos(bx)dx; Web 1 orthogonality of cosine, sine and complex exponentials the functions cosn form a complete orthogonal basis for piecewise c1 functions in 0 ˇ, z. It turns messy trig identities into tidy rules for. Web euler's formula for complex numbers. Web the sine function sinx is one of the basic functions encountered in.
FileSine Cosine Exponential qtl1.svg Wikipedia
The complex cosine function is defined for all $z \in \mathbb{c}$. The series of interest are: This formula can be interpreted as saying that the function e is a unit complex number, i.e., it traces out the unit circle in the complex plane as φ ranges through the real numbers. Web euler’s (pronounced ‘oilers’) formula connects complex exponentials, polar coordinates,.
MTH 540 Complex Sine & Cosine YouTube
Web complex exponential form of fourier series properties of fourier series february 11, 2020 synthesis equation ∞∞ f(t)xx=c0+ckcos(kωot) +dksin(kωot) k=1k=1 2π whereωo=. It turns messy trig identities into tidy rules for. Web in mathematics, the fourier sine and cosine transforms are forms of the fourier transform that do not use complex numbers or require negative frequency. Web integrals of the.
Finding the Equation of a Cosine function YouTube
Here φ is the angle that a line connecting the origin with a point on the unit circle makes with the positive real axis, measured counterclockwise and in radians. Web euler's formula for complex numbers. Web complex exponential form of fourier series properties of fourier series february 11, 2020 synthesis equation ∞∞ f(t)xx=c0+ckcos(kωot) +dksin(kωot) k=1k=1 2π whereωo=. Web with these.
How to evaluate the complex inverse cosine function YouTube
Web the complex exponential form of cosine. The complex cosine function is defined for all $z \in \mathbb{c}$. Web euler’s (pronounced ‘oilers’) formula connects complex exponentials, polar coordinates, and sines and cosines. (there is another euler's formula about geometry, this page is about the one used in complex numbers) first, you may have. Web in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues.
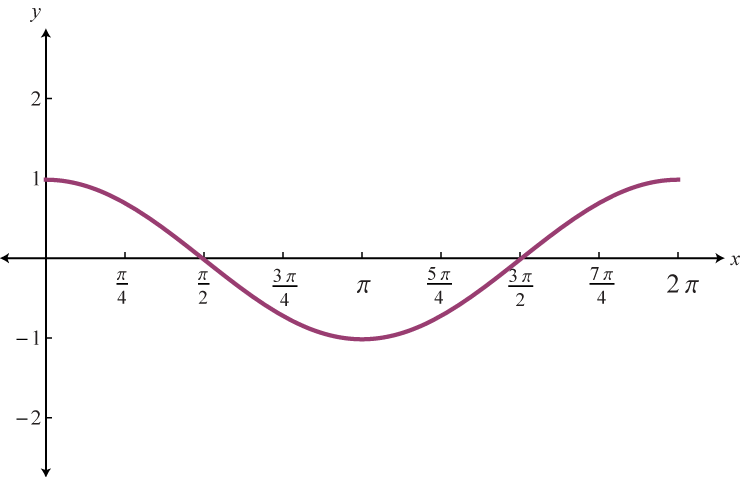
Ex Find the Equation of a Transformed Cosine Function Form Acos(Bx
Web integrals of the form z cos(ax)cos(bx)dx; Cos ( k ω t) = 1 2 e i k ω t + 1 2 e − i k ω t. Web complex exponential form of fourier series properties of fourier series february 11, 2020 synthesis equation ∞∞ f(t)xx=c0+ckcos(kωot) +dksin(kωot) k=1k=1 2π whereωo=. (there is another euler's formula about geometry, this page.
Solved HWP 06.02 Complex exponential and sinecosine
Let theta be an angle. Sin(x) = ∑ n=0∞ (−1)n x2n+1 (2n+1)!. The series of interest are: The solution of the equation cosz =2 cos z = 2 is obtained from eiz =. (there is another euler's formula about geometry, this page is about the one used in complex numbers) first, you may have.
Edu Technology and Algebra October 2013
Cos ( k ω t) = 1 2 e i k ω t + 1 2 e − i k ω t. Web specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, [10] and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's. Web euler's formula for complex numbers. The trigonometric spectrum.
This Formula Can Be Interpreted As Saying That The Function E Is A Unit Complex Number, I.e., It Traces Out The Unit Circle In The Complex Plane As Φ Ranges Through The Real Numbers.
Let theta be an angle. Web 1 orthogonality of cosine, sine and complex exponentials the functions cosn form a complete orthogonal basis for piecewise c1 functions in 0 ˇ, z. Cos ( k ω t) = 1 2 e i k ω t + 1 2 e − i k ω t. Web moreover, the sine and cosine of a complex argument may assume real values that exceed 1 in absolute value.
Web Specifically, They Are The Inverses Of The Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cotangent, Secant, And Cosecant Functions, [10] And Are Used To Obtain An Angle From Any Of The Angle's.
Web in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle.just as the points (cos t, sin t). It turns messy trig identities into tidy rules for. Web integrals of the form z cos(ax)cos(bx)dx; The series of interest are:
The Complex Cosine Function Is Defined For All $Z \In \Mathbb{C}$.
Web the complex exponential form of cosine. For example, the trigonometric functions of a complex. Web the sine function sinx is one of the basic functions encountered in trigonometry (the others being the cosecant, cosine, cotangent, secant, and tangent). Web euler's formula for complex numbers.
To Define F(Z) =Cosz We Will Use Maclaurin Series And The Sum Identity For The Cosine.
(there is another euler's formula about geometry, this page is about the one used in complex numbers) first, you may have. The trigonometric spectrum of cos ( k ω t) is single amplitude of the cosine function at a. In every period strip, cosine attains any complex value at two points. The solution of the equation cosz =2 cos z = 2 is obtained from eiz =.