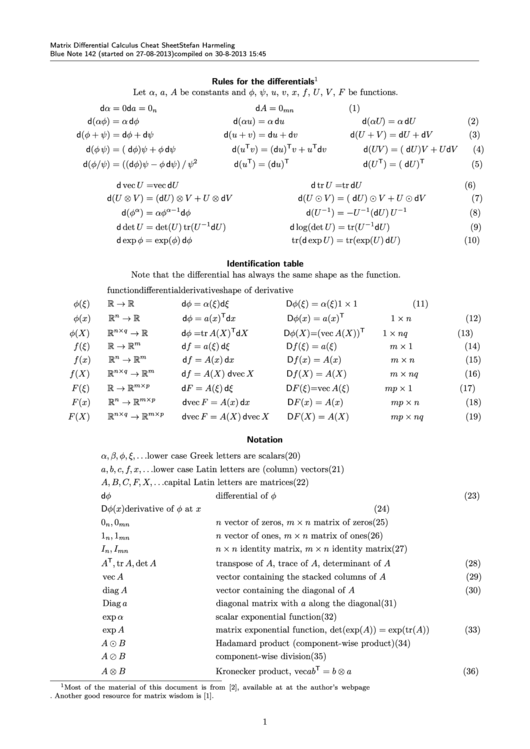
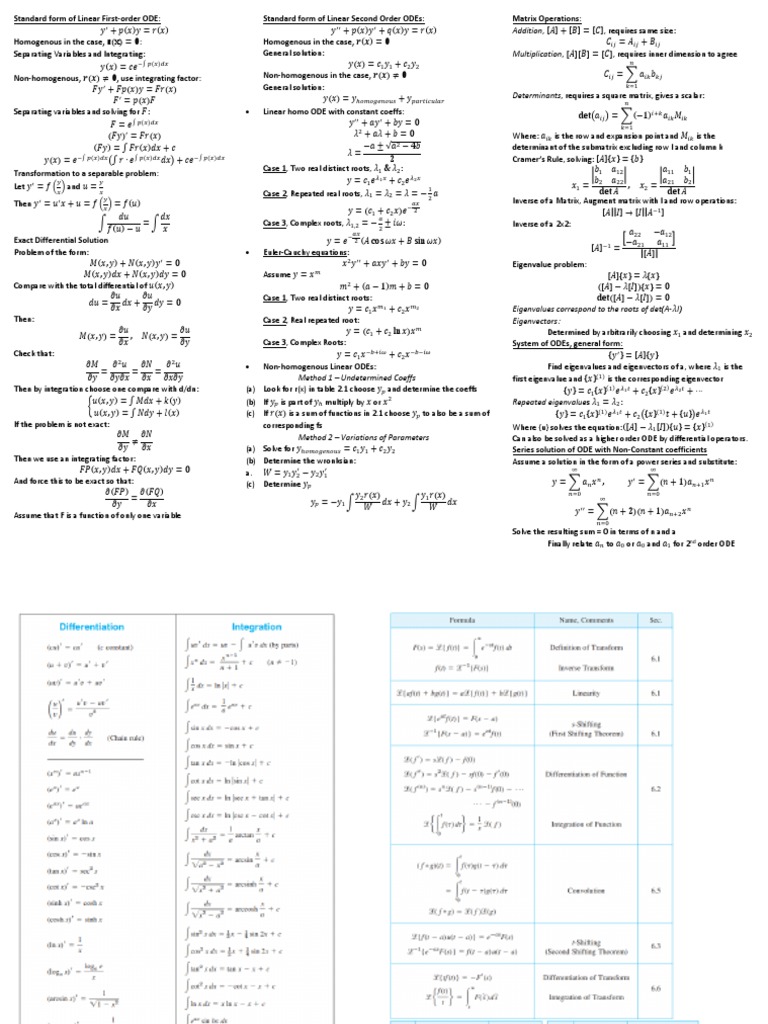
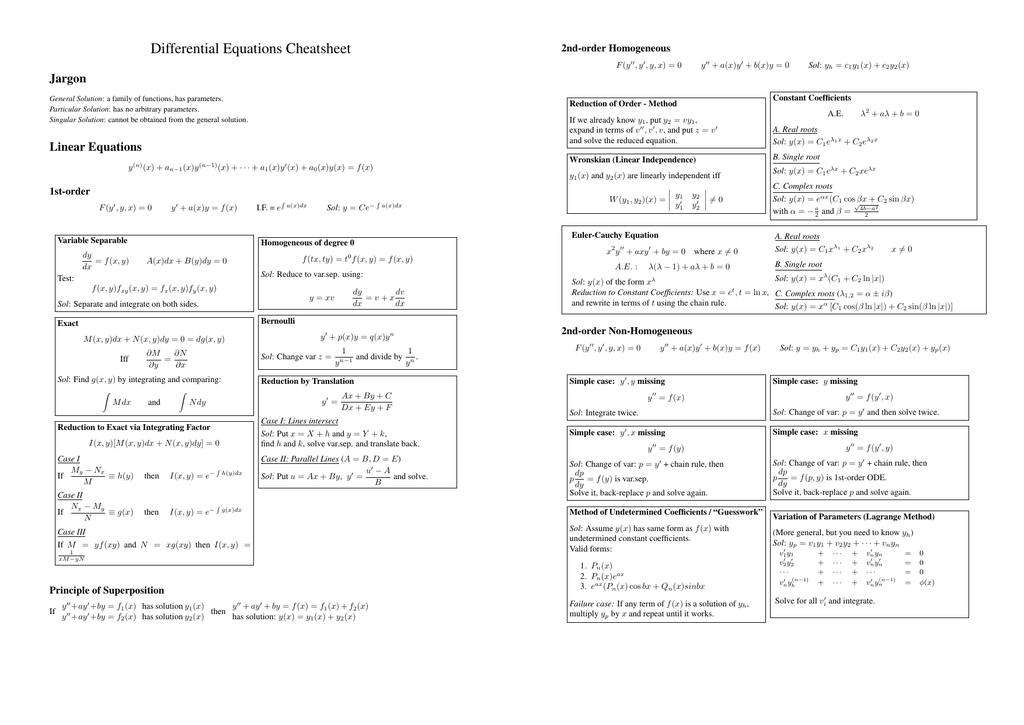
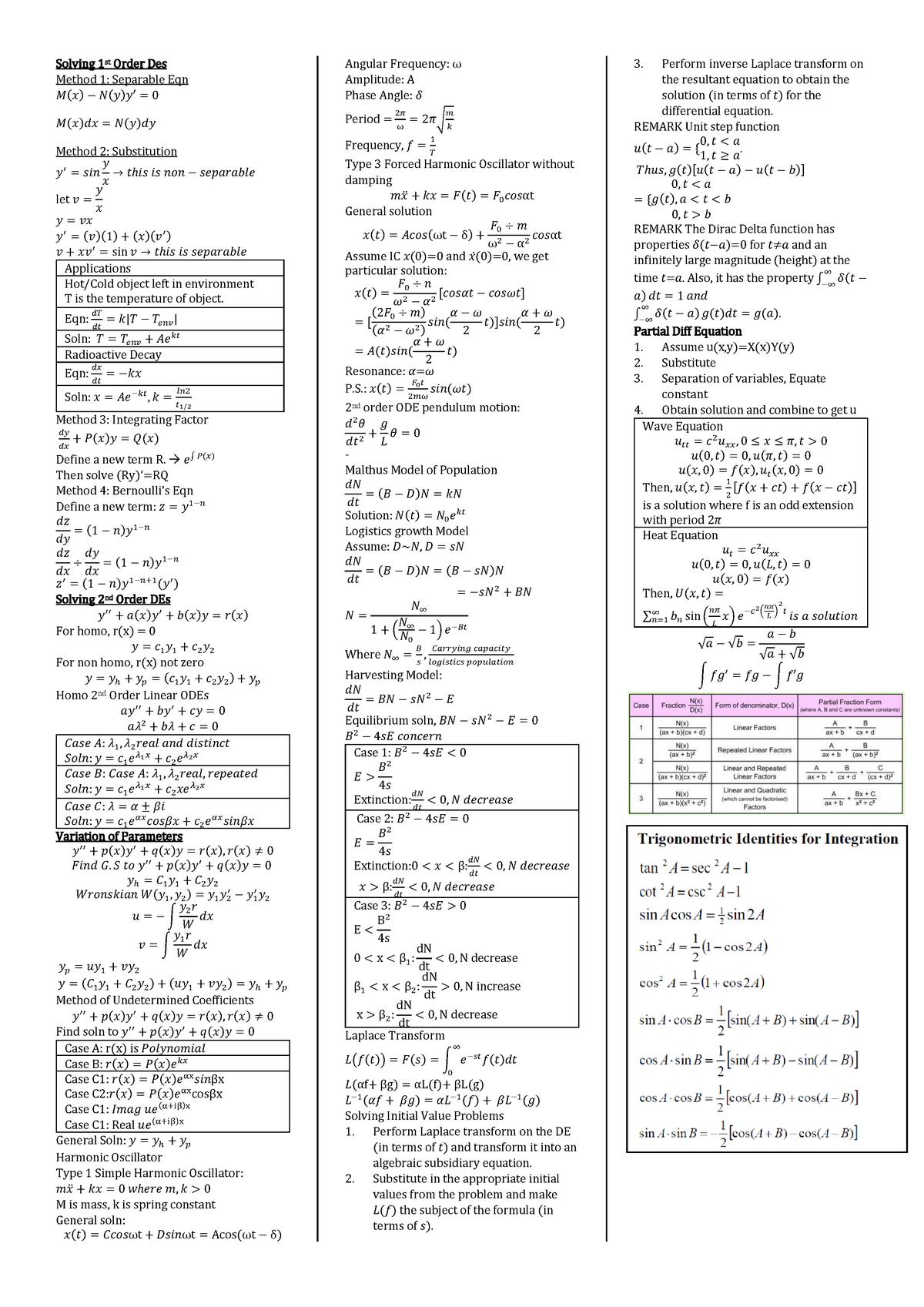
Differential Equations Cheat Sheet
Differential Equations Cheat Sheet - Web classifying differential equations by order. The order of a differential equation simply is. Web a differential equation is linear if it is linear in parameters such that the coefficients on each deriviative of y term is a function of the independent variable (t). Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p ( t) y = g ( t). The most common classification of differential equations is based on order. Web equation, then multiply the guess by xk, where kis the smallest positive integer such that no term in xkyp(x) is a solution of the homogeneous problem.
Web a differential equation is linear if it is linear in parameters such that the coefficients on each deriviative of y term is a function of the independent variable (t). Web classifying differential equations by order. The most common classification of differential equations is based on order. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p ( t) y = g ( t). Web equation, then multiply the guess by xk, where kis the smallest positive integer such that no term in xkyp(x) is a solution of the homogeneous problem. The order of a differential equation simply is.
The most common classification of differential equations is based on order. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p ( t) y = g ( t). Web a differential equation is linear if it is linear in parameters such that the coefficients on each deriviative of y term is a function of the independent variable (t). The order of a differential equation simply is. Web classifying differential equations by order. Web equation, then multiply the guess by xk, where kis the smallest positive integer such that no term in xkyp(x) is a solution of the homogeneous problem.
Equation Cheat Sheet PDF Equations Rates
Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p ( t) y = g ( t). Web a differential equation is linear if it is linear in parameters such that the coefficients on each deriviative of y term is a function of the independent variable (t). Web equation, then multiply the guess by xk, where kis.
Matrix Differential Calculus Cheat Sheet printable pdf download
The order of a differential equation simply is. Web classifying differential equations by order. Web equation, then multiply the guess by xk, where kis the smallest positive integer such that no term in xkyp(x) is a solution of the homogeneous problem. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p ( t) y = g (.
Engineering Mathematics Cheat Sheet Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Web equation, then multiply the guess by xk, where kis the smallest positive integer such that no term in xkyp(x) is a solution of the homogeneous problem. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p ( t) y = g ( t). The most common classification of differential equations is based on order. Web a.
MA1512 Cheatsheet Summary Differential Equations for Engineering 1
Web a differential equation is linear if it is linear in parameters such that the coefficients on each deriviative of y term is a function of the independent variable (t). The order of a differential equation simply is. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p ( t) y = g ( t). Web classifying.
Differential Equations Cheatsheet
Web equation, then multiply the guess by xk, where kis the smallest positive integer such that no term in xkyp(x) is a solution of the homogeneous problem. The order of a differential equation simply is. The most common classification of differential equations is based on order. Web a differential equation is linear if it is linear in parameters such that.
calculus cheat sheet Cheat sheet calculus machine learning series math
Web classifying differential equations by order. The most common classification of differential equations is based on order. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p ( t) y = g ( t). Web equation, then multiply the guess by xk, where kis the smallest positive integer such that no term in xkyp(x) is a solution.
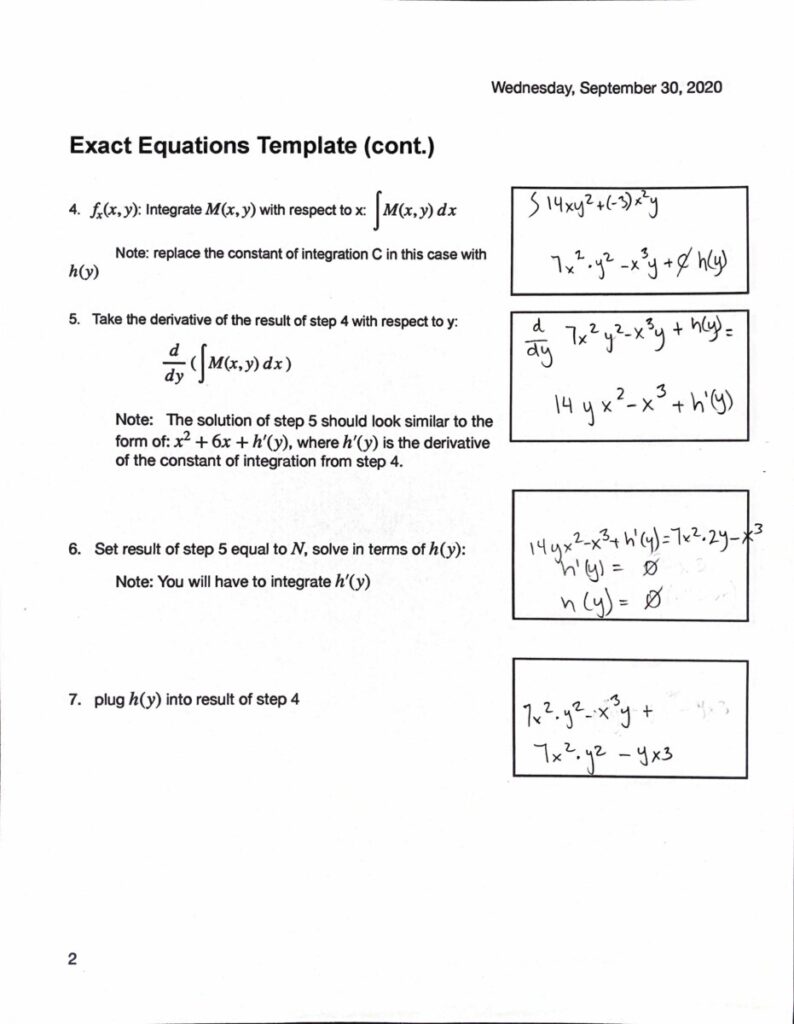
Exact Equations Cheat Sheet MAT2680 Differential Equations
Web classifying differential equations by order. The most common classification of differential equations is based on order. Web a differential equation is linear if it is linear in parameters such that the coefficients on each deriviative of y term is a function of the independent variable (t). Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p.
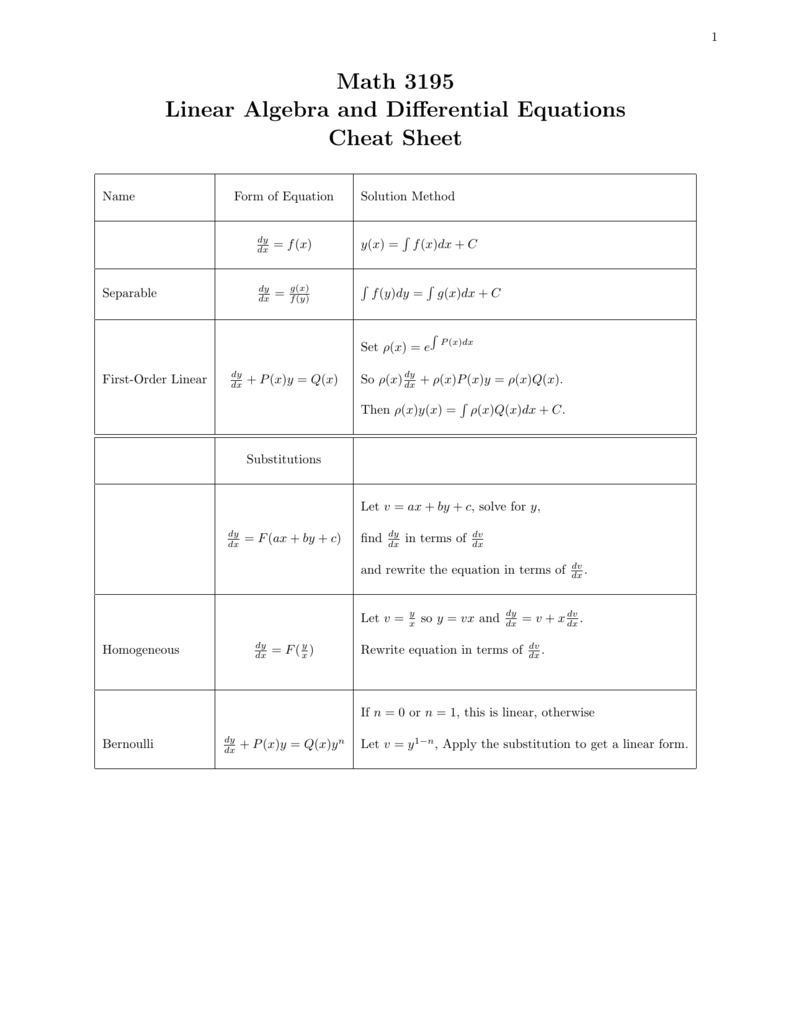
Math 3195 Linear Algebra and Differential Equations Cheat Sheet
Web classifying differential equations by order. Web a differential equation is linear if it is linear in parameters such that the coefficients on each deriviative of y term is a function of the independent variable (t). The order of a differential equation simply is. Web equation, then multiply the guess by xk, where kis the smallest positive integer such that.
Differential Equations Cheat Sheet Payhip
The order of a differential equation simply is. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p ( t) y = g ( t). The most common classification of differential equations is based on order. Web a differential equation is linear if it is linear in parameters such that the coefficients on each deriviative of y.
differentiation cheat sheet Google Search Calculus, Cheat sheets
Web a differential equation is linear if it is linear in parameters such that the coefficients on each deriviative of y term is a function of the independent variable (t). The order of a differential equation simply is. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p ( t) y = g ( t). Web classifying.
The Most Common Classification Of Differential Equations Is Based On Order.
Web equation, then multiply the guess by xk, where kis the smallest positive integer such that no term in xkyp(x) is a solution of the homogeneous problem. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y = g(t) y ′ + p ( t) y = g ( t). Web classifying differential equations by order. Web a differential equation is linear if it is linear in parameters such that the coefficients on each deriviative of y term is a function of the independent variable (t).