Reduced Form Of Nadh
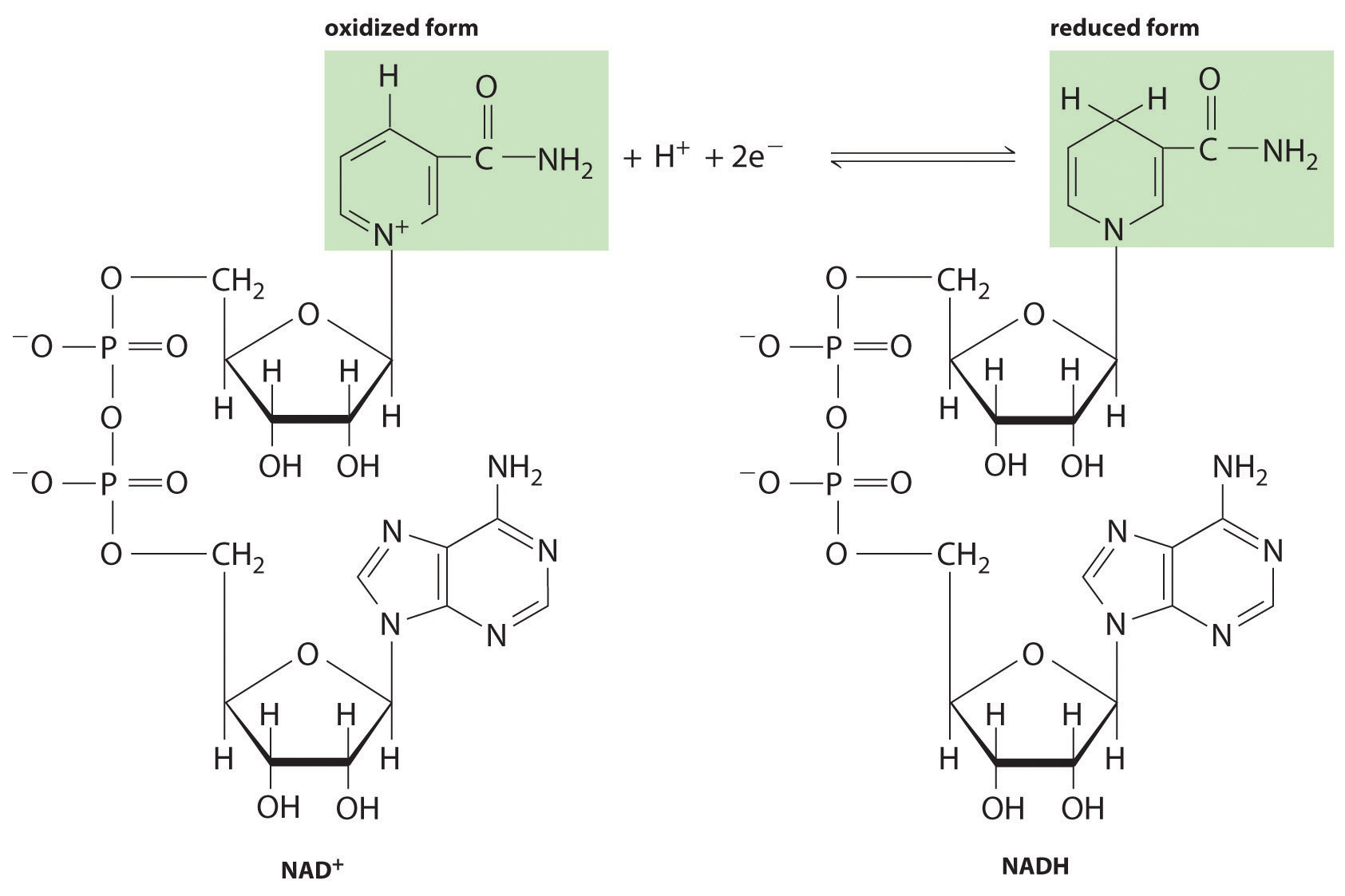
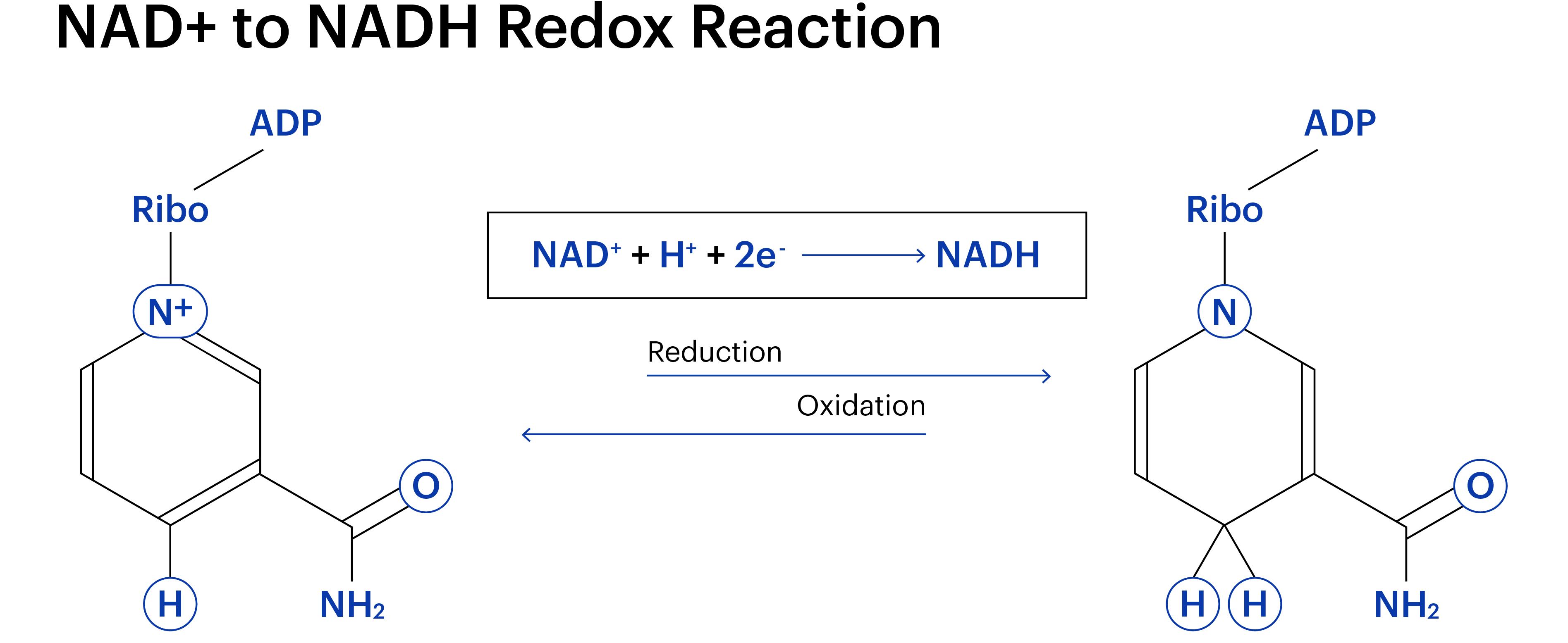
Reduced Form Of Nadh - Nad + is an oxidizing agent, accepting electrons from other molecules and becoming reduced; Nrh acts as a more potent and faster nad + precursor than nr in mammalian cells and tissues. American heritage® dictionary of the english language, fifth edition. Some people take it in supplement form to treat chronic fatigue syndrome (also known as myalgic encephalomyelitis or me/cfs ). Web nadh definition, an abbreviation for the reduced form of nad in electron transport reactions. It has an absorption maximum of 340 nm and an emission maximum at 465 nm. The term oxidized can be misleading, though, as it does not necessarily require oxygen. It exists in two forms, that is oxidized form (nad+) and reduced form (nadh). It carries electrons from one reaction to other. Web nad + is the oxidized form of the molecule;
Web nadh definition, an abbreviation for the reduced form of nad in electron transport reactions. Nadh reduces the flavin, which in turn reduces the sulfenic acid to a thiol. Web in cellular metabolism, nad is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another, so it is found in two forms: Nadh helps your body make energy. The full form of nad is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Web nad + is the oxidized form of the molecule; Nad+ is the oxidized form of nadh. They are redox partners in hundreds of cellular enzymatic reactions. Web nad + can be reduced into nadh in the metabolic processes, including glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation and the tca cycle. With h +, this reaction forms nadh, which can be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons.
It has an absorption maximum of 340 nm and an emission maximum at 465 nm. Web nadh is bound to a hydride and nad+ is not bound to a hydride. This enables energy generation through glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration to support cell growth and survival. It carries electrons from one reaction to other. Standard solutions of nadh gave the following fluorescence intensities: Web the sulfenic acid is first reduced to the thiol by nadh via the flavin (scheme 18). It exists in two forms, that is oxidized form (nad+) and reduced form (nadh). Web the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nadh) is an important and highly fluorescent coenzyme. Web nad + is the oxidized form of the molecule; Nrh acts as a more potent and faster nad + precursor than nr in mammalian cells and tissues.
NADH Nicotinammide Adenina Dinucleotide Alzheimer Italia
Web the sulfenic acid is first reduced to the thiol by nadh via the flavin (scheme 18). (a) construct a spreadsheet and use it to draw a calibration curve for nadh. This enables energy generation through glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration to support cell growth and survival. Nad + is an oxidizing agent, accepting electrons from other molecules and becoming reduced;.
Why NAD+ Declines during Aging It’s Destroyed
The enzyme then binds another molecule of nadh while the active site cysteine is a thiol. Web nadh, or reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide , is a chemical made in your body from niacin, a type of b vitamin. The objective of the study was to determine both the toxicity of the stabilized orally absorbable form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nadh).
hillis2e_ch06
Web nad + can be reduced into nadh in the metabolic processes, including glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation and the tca cycle. Some people take it in supplement form to treat chronic fatigue syndrome (also known as myalgic encephalomyelitis or me/cfs ). It is the reduced form of nadp + and as such is a high energy. Web nadh, or reduced.
ReducingNAD PhD Muscle
1 apart from its role as a redox cofactor, during the last decade nad +. Web all life forms require nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, nad +, and its reduced form nadh. Nadh helps your body make energy. It has vital role in energy production via redox reaction. Nad+ is the oxidized form of nadh.
RPI NADH (BNicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, Reduced Form, Disodium
These two forms of nad are known as a redox couple, a term that is used to describe a reduced (the red in redox) and oxidized (the ox in redox) form of the same atom or molecule. Web nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad+) and its reduced form nadh are essential coupled redox metabolites that primarily promote cellular oxidative (catabolic) metabolic reactions..
Solved The Reduced Form Of The Coenzyme Nicotinamide Aden...
Fad+ is flavin adenine dinucleotide. Changes in the intracellular levels of total nad (nad + + nadh) and the (nad + /nadh) ratio can cause cellular dysfunction. It has vital role in energy production via redox reaction. The reduced form of nad. The reduced form of nad.
NADH And NADPH The Coenzymes That Help Plants Convert Light Energy
Nad + is an oxidizing agent, accepting electrons from other molecules and becoming reduced; The enzyme then binds another molecule of nadh while the active site cysteine is a thiol. Nrh acts as a more potent and faster nad + precursor than nr in mammalian cells and tissues. It is the reduced form of nadp + and as such is.
Thermodynamics and Life
Fad+ is flavin adenine dinucleotide. The term oxidized can be misleading, though, as it does not necessarily require oxygen. Some people take it in supplement form to treat chronic fatigue syndrome (also known as myalgic encephalomyelitis or me/cfs ). It is a cofactor that is found in living cells. • nrh is orally bioavailable and not degraded in plasma.
1 Nadh Is Equal To How Many Atp Wasfa Blog
Visit to know long meaning of nadh acronym and abbreviations. • nrh is orally bioavailable and not degraded in plasma. Web nadh synonyms, nadh pronunciation, nadh translation, english dictionary definition of nadh. The reduced form of nad. Web nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate or nadph is a reduced coenzyme that plays a key role in the synthesis of carbohydrates in photosynthetic.
NADH Reviews What Is The Function of NADH In Your Body
Web in cellular metabolism, nad is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another, so it is found in two forms: Standard solutions of nadh gave the following fluorescence intensities: Web nadh, or reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide , is a chemical made in your body from niacin, a type of b vitamin. Nadh, in turn, drives the.
Some People Take It In Supplement Form To Treat Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (Also Known As Myalgic Encephalomyelitis Or Me/Cfs ).
These two forms of nad are known as a redox couple, a term that is used to describe a reduced (the red in redox) and oxidized (the ox in redox) form of the same atom or molecule. It is a cofactor that is found in living cells. It has an absorption maximum of 340 nm and an emission maximum at 465 nm. With h +, this reaction forms nadh, which can be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons.
• Nrh Is Orally Bioavailable And Not Degraded In Plasma.
Web nad + can be reduced into nadh in the metabolic processes, including glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation and the tca cycle. Web the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nadh) is an important and highly fluorescent coenzyme. Web the sulfenic acid is first reduced to the thiol by nadh via the flavin (scheme 18). Nadh is the reduced form of nad+.
Web In Cellular Metabolism, Nad Is Involved In Redox Reactions, Carrying Electrons From One Reaction To Another, So It Is Found In Two Forms:
The term oxidized can be misleading, though, as it does not necessarily require oxygen. Web all life forms require nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, nad +, and its reduced form nadh. Nadh, in turn, drives the generation of atp via oxphos, the production of. Subscribe to america's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and.
Web Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Or Nadph Is A Reduced Coenzyme That Plays A Key Role In The Synthesis Of Carbohydrates In Photosynthetic Organisms.
Web nad + is the oxidized form of the molecule; The full form of nad is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Fad+ is flavin adenine dinucleotide. Web nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad+) and its reduced form nadh are essential coupled redox metabolites that primarily promote cellular oxidative (catabolic) metabolic reactions.