Sine And Cosine Exponential Form
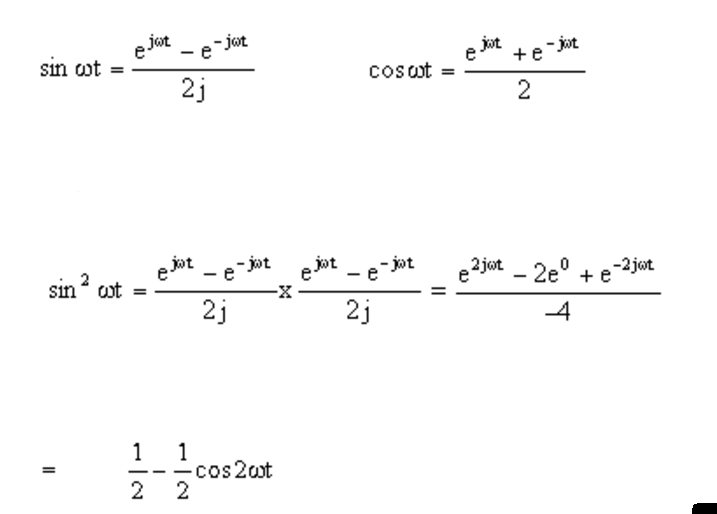
Sine And Cosine Exponential Form - Web we can use euler’s theorem to express sine and cosine in terms of the complex exponential function as s i n c o s 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑖 𝑒 − 𝑒 , 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑒 + 𝑒. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. Y = acos(kx) + bsin(kx) according to my notes, this can also be written. Web conversion from exponential to cosine asked 7 years, 8 months ago modified 7 years, 8 months ago viewed 12k times 2 i'm trying to understand the following. Web specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, [10] and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's. Web i am in the process of doing a physics problem with a differential equation that has the form: Z cos(ax)sin(bx)dx or z sin(ax)sin(bx)dx are usually done by using the addition formulas for the cosine and sine functions. By thinking of the sine and cosine values as coordinates. Using these formulas, we can derive further. Fourier series coefficients are discussed for real signals.
Fourier series coefficients are discussed for real signals. Web up to 5% cash back to represent the fourier series in concise form, the sine and cosine terms of trigonometric form, the fourier series are expressed in terms of exponential function. As a result, the other hyperbolic functions are meromorphic in the whole complex plane. Let be an angle measured. Web today, we derive the complex exponential definitions of the sine and cosine function, using euler's formula. Web we can use euler’s theorem to express sine and cosine in terms of the complex exponential function as s i n c o s 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑖 𝑒 − 𝑒 , 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑒 + 𝑒. Web the exponential form of fourier series is presented from which the sine cosine form is derived. It is not currently accepting answers. Z cos(ax)sin(bx)dx or z sin(ax)sin(bx)dx are usually done by using the addition formulas for the cosine and sine functions. Y = acos(kx) + bsin(kx) according to my notes, this can also be written.
(45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. By thinking of the sine and cosine values as coordinates. Web today, we derive the complex exponential definitions of the sine and cosine function, using euler's formula. Web we can use euler’s theorem to express sine and cosine in terms of the complex exponential function as s i n c o s 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑖 𝑒 − 𝑒 , 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑒 + 𝑒. Y = acos(kx) + bsin(kx) according to my notes, this can also be written. The sine function is one of the basic functions encountered in trigonometry (the others being the cosecant, cosine , cotangent, secant, and tangent ). Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. Web the exponential form of fourier series is presented from which the sine cosine form is derived. Web conversion from exponential to cosine asked 7 years, 8 months ago modified 7 years, 8 months ago viewed 12k times 2 i'm trying to understand the following. Z cos(ax)sin(bx)dx or z sin(ax)sin(bx)dx are usually done by using the addition formulas for the cosine and sine functions.
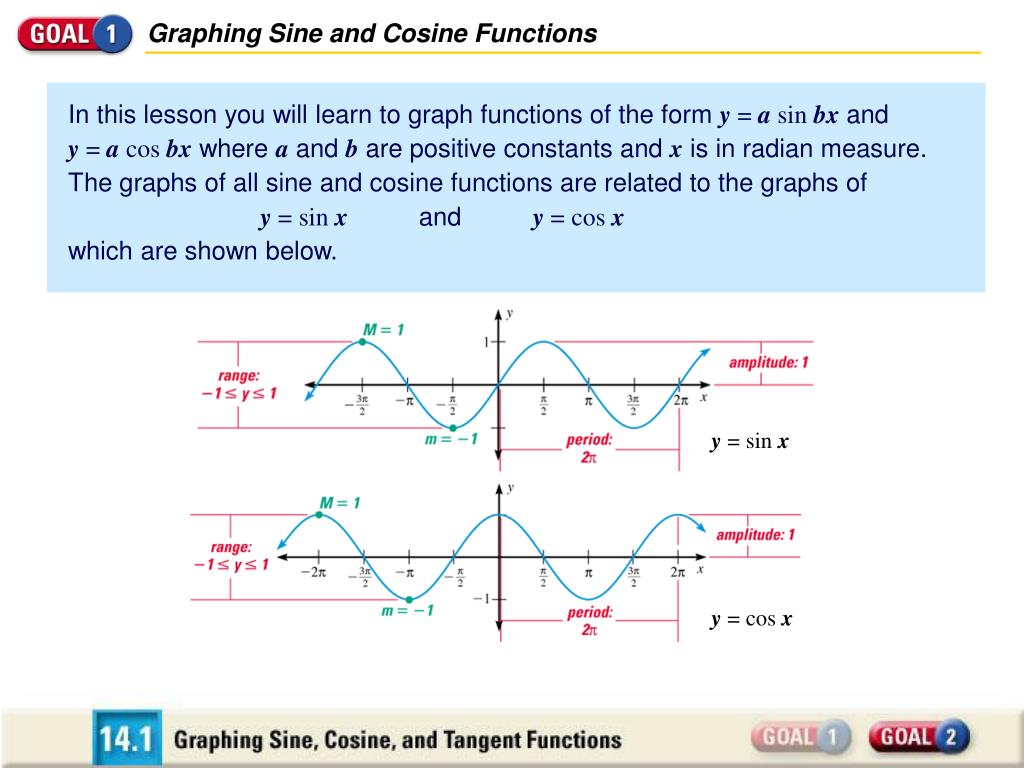
PPT Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions PowerPoint Presentation, free
It is not currently accepting answers. Web conversion from exponential to cosine asked 7 years, 8 months ago modified 7 years, 8 months ago viewed 12k times 2 i'm trying to understand the following. Web i am in the process of doing a physics problem with a differential equation that has the form: Z cos(ax)sin(bx)dx or z sin(ax)sin(bx)dx are usually.
Relationship between sine, cosine and exponential function
Web i am in the process of doing a physics problem with a differential equation that has the form: Web we can use euler’s theorem to express sine and cosine in terms of the complex exponential function as s i n c o s 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑖 𝑒 − 𝑒 , 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑒 + 𝑒..
Function For Sine Wave Between Two Exponential Cuves Mathematics
Web conversion from exponential to cosine asked 7 years, 8 months ago modified 7 years, 8 months ago viewed 12k times 2 i'm trying to understand the following. It is not currently accepting answers. Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. Web today, we derive the complex exponential definitions of the sine and cosine function, using euler's formula. Web.
Question Video Converting the Product of Complex Numbers in Polar Form
By thinking of the sine and cosine values as coordinates. The sine function is one of the basic functions encountered in trigonometry (the others being the cosecant, cosine , cotangent, secant, and tangent ). Let be an angle measured. Web today, we derive the complex exponential definitions of the sine and cosine function, using euler's formula. Web relations between cosine,.
Basics of QPSK modulation and display of QPSK signals Electrical
Z cos(ax)sin(bx)dx or z sin(ax)sin(bx)dx are usually done by using the addition formulas for the cosine and sine functions. As a result, the other hyperbolic functions are meromorphic in the whole complex plane. Web the hyperbolic sine and the hyperbolic cosine are entire functions. Web i am in the process of doing a physics problem with a differential equation that.
Write Equations Of Sine Functions Using Properties Calculator
Web conversion from exponential to cosine asked 7 years, 8 months ago modified 7 years, 8 months ago viewed 12k times 2 i'm trying to understand the following. Web euler’s formula for complex exponentials according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and. This question does not appear to be about.
complex numbers Converting i to exponential form Mathematics
Fourier series coefficients are discussed for real signals. Web we can use euler’s theorem to express sine and cosine in terms of the complex exponential function as s i n c o s 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑖 𝑒 − 𝑒 , 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑒 + 𝑒. Web i am in the process of doing a physics problem.
Sine and cosine problems Math Tutoring & Exercises
It is not currently accepting answers. Web conversion from exponential to cosine asked 7 years, 8 months ago modified 7 years, 8 months ago viewed 12k times 2 i'm trying to understand the following. This question does not appear to be about electronics design within the scope defined in. As a result, the other hyperbolic functions are meromorphic in the.
Other Math Archive January 29, 2018
Web the hyperbolic sine and the hyperbolic cosine are entire functions. Using these formulas, we can derive further. Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. As a result, the other hyperbolic functions are meromorphic in the whole complex plane. Web integrals of the form z cos(ax)cos(bx)dx;
EM to Optics 10 Converting Cos & Sine to Complex Exponentials YouTube
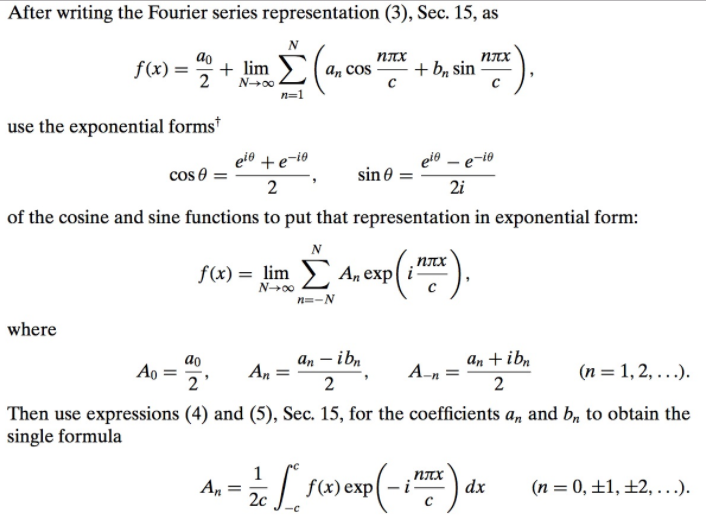
Web up to 5% cash back to represent the fourier series in concise form, the sine and cosine terms of trigonometric form, the fourier series are expressed in terms of exponential function. By thinking of the sine and cosine values as coordinates. Web we can use euler’s theorem to express sine and cosine in terms of the complex exponential function.
Using These Formulas, We Can Derive Further.
Let be an angle measured. Web up to 5% cash back to represent the fourier series in concise form, the sine and cosine terms of trigonometric form, the fourier series are expressed in terms of exponential function. Web integrals of the form z cos(ax)cos(bx)dx; Web i am in the process of doing a physics problem with a differential equation that has the form:
Web Today, We Derive The Complex Exponential Definitions Of The Sine And Cosine Function, Using Euler's Formula.
Web conversion from exponential to cosine asked 7 years, 8 months ago modified 7 years, 8 months ago viewed 12k times 2 i'm trying to understand the following. By thinking of the sine and cosine values as coordinates. The sine function is one of the basic functions encountered in trigonometry (the others being the cosecant, cosine , cotangent, secant, and tangent ). Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions.
Web The Exponential Form Of Fourier Series Is Presented From Which The Sine Cosine Form Is Derived.
This question does not appear to be about electronics design within the scope defined in. Fourier series coefficients are discussed for real signals. Web the hyperbolic sine and the hyperbolic cosine are entire functions. It is not currently accepting answers.
Z Cos(Ax)Sin(Bx)Dx Or Z Sin(Ax)Sin(Bx)Dx Are Usually Done By Using The Addition Formulas For The Cosine And Sine Functions.
Web specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, [10] and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's. As a result, the other hyperbolic functions are meromorphic in the whole complex plane. Web we can use euler’s theorem to express sine and cosine in terms of the complex exponential function as s i n c o s 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑖 𝑒 − 𝑒 , 𝜃 = 1 2 𝑒 + 𝑒. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all.