Where And In What Form Is Prokaryotic Dna Found
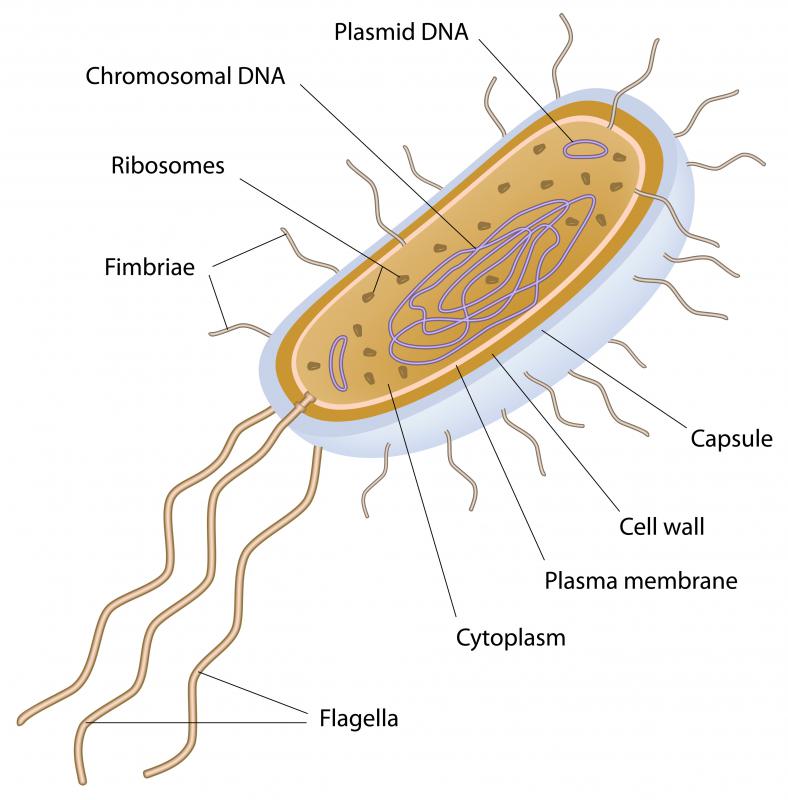
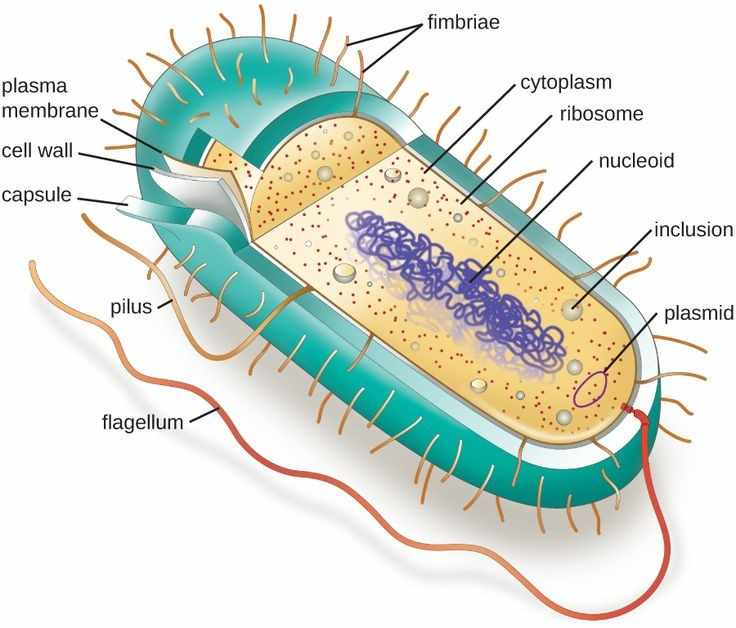
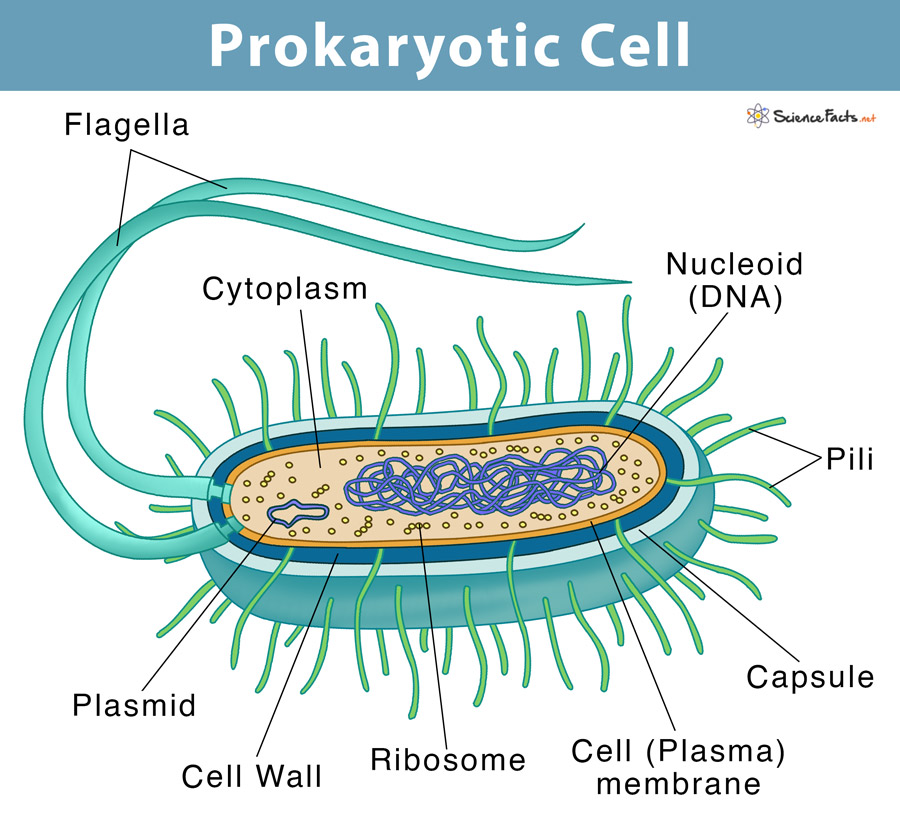
Where And In What Form Is Prokaryotic Dna Found - Web prokaryotic dna replication is the process by which a prokaryote duplicates its dna into another copy that is passed on to daughter cells. Web where and in what form is prokaryotic dna found? Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like where is the dna found in a prokaryotic cell?, where is dna found in a eukaryotic cell?, does the prokaryotic cell. It is in long strands bundled in the cell. Therefore, their genetic material (dna) is located in the central region of the cell called the nucleoid.moreover, nucleoid lacks a membrane and is. Its genetic material can be found just floating in the cytoplasm in the form of a coiled loop called a nucleoid. The process of dna replication can be summarized as. Prokaryotic dna can be found in a coiled loop floating in the cytoplasm in a region called the nucleoid. Web dna transfer between prokaryotic cells occurs in bacteria and archaea, although it has been mainly studied in bacteria. Web where is dna found inside prokaryotic cells?
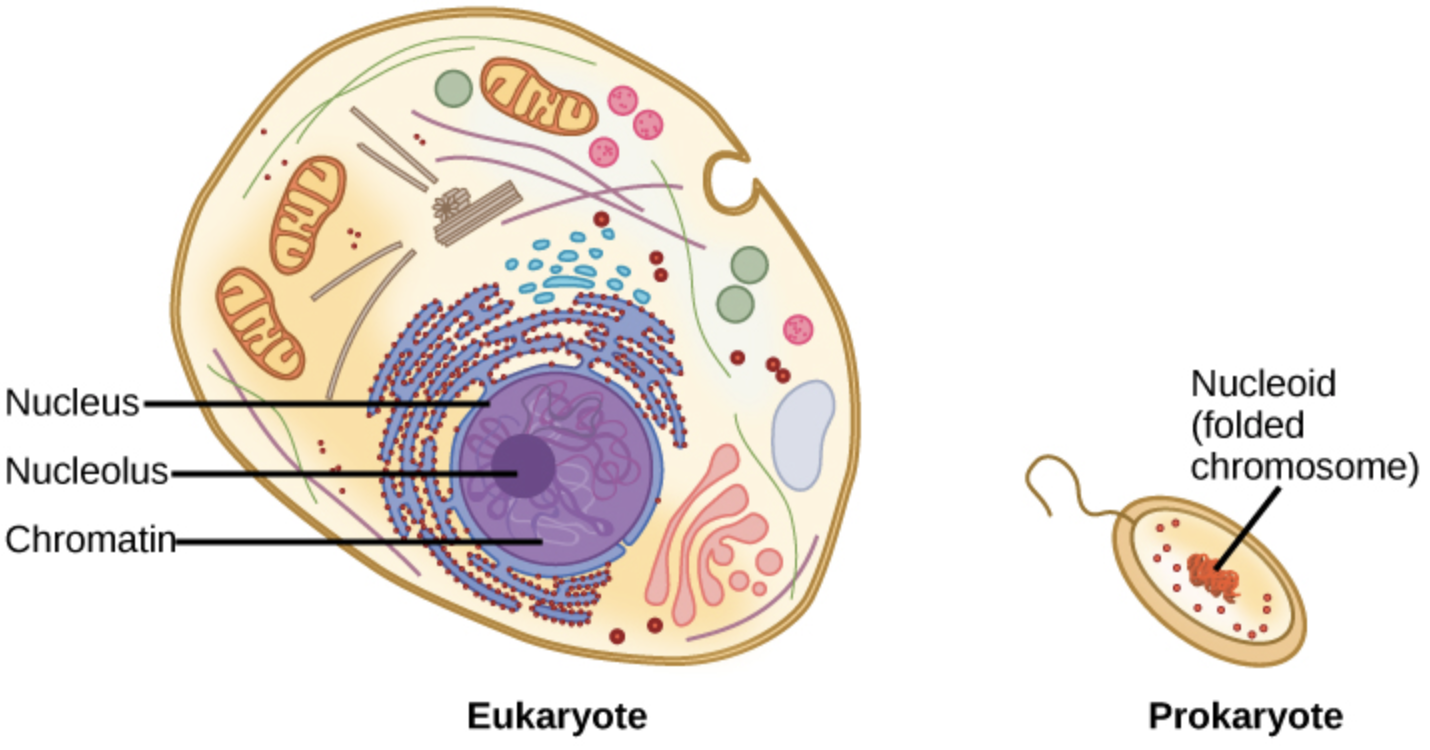
Therefore, their genetic material (dna) is located in the central region of the cell called the nucleoid.moreover, nucleoid lacks a membrane and is. (eukarya, the third, contains all. Web prokaryotic cells have no nucleus; In bacteria, gene transfer occurs by three processes. Prokaryotic dna can be found in a coiled loop floating in the cytoplasm in a region called the nucleoid. Web frequently asked questions what form does dna take in the cell? Dna is found inside prokaryotic cells freely floating in the cytoplasm. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like where is the dna found in a prokaryotic cell?, where is dna found in a eukaryotic cell?, does the prokaryotic cell. Web prokaryotic cells have no nuclear membranes. Web once the chromosome has been completely replicated, the two dna copies move into two different cells during cell division.
Web prokaryotic cells have no nuclear membranes. In addition, prokaryotes have plasmids, which are smaller pieces of circular dna that can replicate separately from. Where is eukaryotic dna found? Web where is dna found inside prokaryotic cells? The process of dna replication can be summarized as. Web dna transfer between prokaryotic cells occurs in bacteria and archaea, although it has been mainly studied in bacteria. (eukarya, the third, contains all. Web 21 rows prokaryotic dna: Web 5 rows most prokaryotic dna is found in their single, circular chromosome. Found freely in the central portion of the cytoplasm.
Reading DNA Packaging in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Biology (Early
Web 5 rows most prokaryotic dna is found in their single, circular chromosome. Therefore, their genetic material (dna) is located in the central region of the cell called the nucleoid.moreover, nucleoid lacks a membrane and is. In addition, prokaryotes have plasmids, which are smaller pieces of circular dna that can replicate separately from. Prokaryotic dna can be found in a.
Prokaryotic Vs. Eukaryotic DNA Replication Dna replication, Dna
In bacteria, gene transfer occurs by three processes. Dna in prokaryotic cells is found in the form of a single circular chromosome in the cytoplasm;. Create a free account to. (eukarya, the third, contains all. Prokaryotic dna can be found in a coiled loop floating in the cytoplasm in a region called the nucleoid.
What Are the Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells?
In bacteria, gene transfer occurs by three processes. Web prokaryotic dna replication is the process by which a prokaryote duplicates its dna into another copy that is passed on to daughter cells. Create a free account to. Web 21 rows prokaryotic dna: Web dna transfer between prokaryotic cells occurs in bacteria and archaea, although it has been mainly studied in.
Structure of Prokaryotes · Biology
The process of dna replication can be summarized as. Web prokaryotic cells have no nucleus; Web once the chromosome has been completely replicated, the two dna copies move into two different cells during cell division. (eukarya, the third, contains all. Web frequently asked questions what form does dna take in the cell?
Unlike eukaryotic cells prokaryotic cells a Lack of class 11 biology CBSE
Web frequently asked questions what form does dna take in the cell? Web prokaryotic cells have no nuclear membranes. In addition, prokaryotes have plasmids, which are smaller pieces of circular dna that can replicate separately from. Web prokaryotes are microscopic organisms belonging to the domains bacteria and archaea, which are two out of the three major domains of life. Prokaryotic.
Pin by Magpie on ชีวะ Prokaryotic cell, Eukaryotic cell, Prokaryotic
Web where is dna found inside prokaryotic cells? Web prokaryotes have no cell nucleus and no membrane enclosed organelles. Web frequently asked questions what form does dna take in the cell? Prokaryotic dna is found in the central part of the. Where is eukaryotic dna found?
Microbiology Definition, Classification & Branches
The process of dna replication can be summarized as. Web frequently asked questions what form does dna take in the cell? Dna in prokaryotic cells is found in the form of a single circular chromosome in the cytoplasm;. Prokaryotic dna can be found in a coiled loop floating in the cytoplasm in a region called the nucleoid. Web prokaryotic cells.
Learn About Prokaryotic Cells, Prokaryotes Bacteria and Archaeans
It is in long strands bundled in the cell. Web prokaryotic cells have no nuclear membranes. In addition, prokaryotes have plasmids, which are smaller pieces of circular dna that can replicate separately from. Therefore, their genetic material (dna) is located in the central region of the cell called the nucleoid.moreover, nucleoid lacks a membrane and is. Web 5 rows most.
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells Similarities & Differences Sciencing
Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like where is the dna found in a prokaryotic cell?, where is dna found in a eukaryotic cell?, does the prokaryotic cell. Web dna transfer between prokaryotic cells occurs in bacteria and archaea, although it has been mainly studied in bacteria. Web 21 rows prokaryotic dna: Web prokaryotes have no cell.
Prokaryotic Cell Definition, Examples, & Structure
Web where and in what form is prokaryotic dna found? Prokaryotic dna can be found in a coiled loop floating in the cytoplasm in a region called the nucleoid. Web prokaryotes are microscopic organisms belonging to the domains bacteria and archaea, which are two out of the three major domains of life. Web 21 rows prokaryotic dna: Web once the.
Web Where Is Dna Found Inside Prokaryotic Cells?
Web dna transfer between prokaryotic cells occurs in bacteria and archaea, although it has been mainly studied in bacteria. Web frequently asked questions what form does dna take in the cell? Web once the chromosome has been completely replicated, the two dna copies move into two different cells during cell division. Web 21 rows prokaryotic dna:
It Is In Long Strands Bundled In The Cell.
Web prokaryotes are microscopic organisms belonging to the domains bacteria and archaea, which are two out of the three major domains of life. Therefore, their genetic material (dna) is located in the central region of the cell called the nucleoid.moreover, nucleoid lacks a membrane and is. Although it is often studied in the model. Web prokaryotic dna replication is the process by which a prokaryote duplicates its dna into another copy that is passed on to daughter cells.
Web Prokaryotes Have No Cell Nucleus And No Membrane Enclosed Organelles.
(eukarya, the third, contains all. Dna is found inside prokaryotic cells freely floating in the cytoplasm. Web prokaryotic cells have no nucleus; In addition, prokaryotes have plasmids, which are smaller pieces of circular dna that can replicate separately from.
The Process Of Dna Replication Can Be Summarized As.
Create a free account to. In bacteria, gene transfer occurs by three processes. Web prokaryotic cells have no nuclear membranes. Found freely in the central portion of the cytoplasm.